Ketamine
Also called K, ket, special K, super K, vitamin K, kitkat
Ketamine is a depressant drug which means that it slows down and interferes with the functioning of the brain and the body. Ketamine is an anaesthetic agent used to provide pain relief during medical procedures. Ketamine is usually manufactured as a liquid for this purpose.
What does it look like?
- Liquid
- Tablet or pill
- Powder
- Swallowed
- Snorted
- Injected
- Smoked
- Suppository
People may use ketamine to induce feelings of euphoria, to feel relaxed, or to experience feelings of dissociation (being detached from the body).
Other short-term effects include:
- Nausea
- Sweating
- Increased heart rate and blood pressure
- Muscle rigidity
- Slurred speech
- Blurred vision
- Confusion
- Hallucinations
- Delusions
- Agitation
- Anxiety
- Paranoia
People who inject are at higher risk of additional harms such as:
- Blood-borne viruses
- Bacterial and fungal infection
- Damage to the circulatory system
- Increased likelihood of overdose
Ketamine affects people differently depending on a range of factors including, how strong it is, how much is consumed, whether it is used with other drugs, and the individual characteristics of the person. Ketamine, when mixed with alcohol and other drugs, increases the risk of an overdose. It is important to know that there is no safe level of use.
- Serious bladder problems
- Kidney problems
- Intense abdominal pain
- Mood and personality changes
- Anxiety
- Depression
- Paranoia
People who are concerned about their ketamine use should talk to their doctor or health professional.
- Spending a great deal of time getting, using, or recovering from the effects
- Using in greater amounts, or for longer than originally planned
- Needing to use more to get the same effect
- Having cravings, difficulties stopping/reducing use
- Experiencing withdrawal symptoms
- Social problems including relationship issues, financial problems, impacts on study or work and legal problems
Sometimes it can take a few attempts to cut back or stop.
- Focus on reasons for cutting down or stopping
- Avoid ‘triggers’ (i.e. things associated with using such as places, people, and stressful situations)
- Ask a friend, family member, or health professional for support
Adis 24/7 Alcohol and Drug Support is a 24 hour, 7 day a week confidential support service for people in Queensland with alcohol and other drug concerns, their loved ones and health professionals.
Talk to us. Anytime, anywhere.
1800 177 833
Signs of a ketamine overdose may include:
- Vomiting
- Loss of consciousness
- Slow breathing
- Dissociation and hallucinations
- Confusion
- Agitation
- Anxiety
- Paranoia
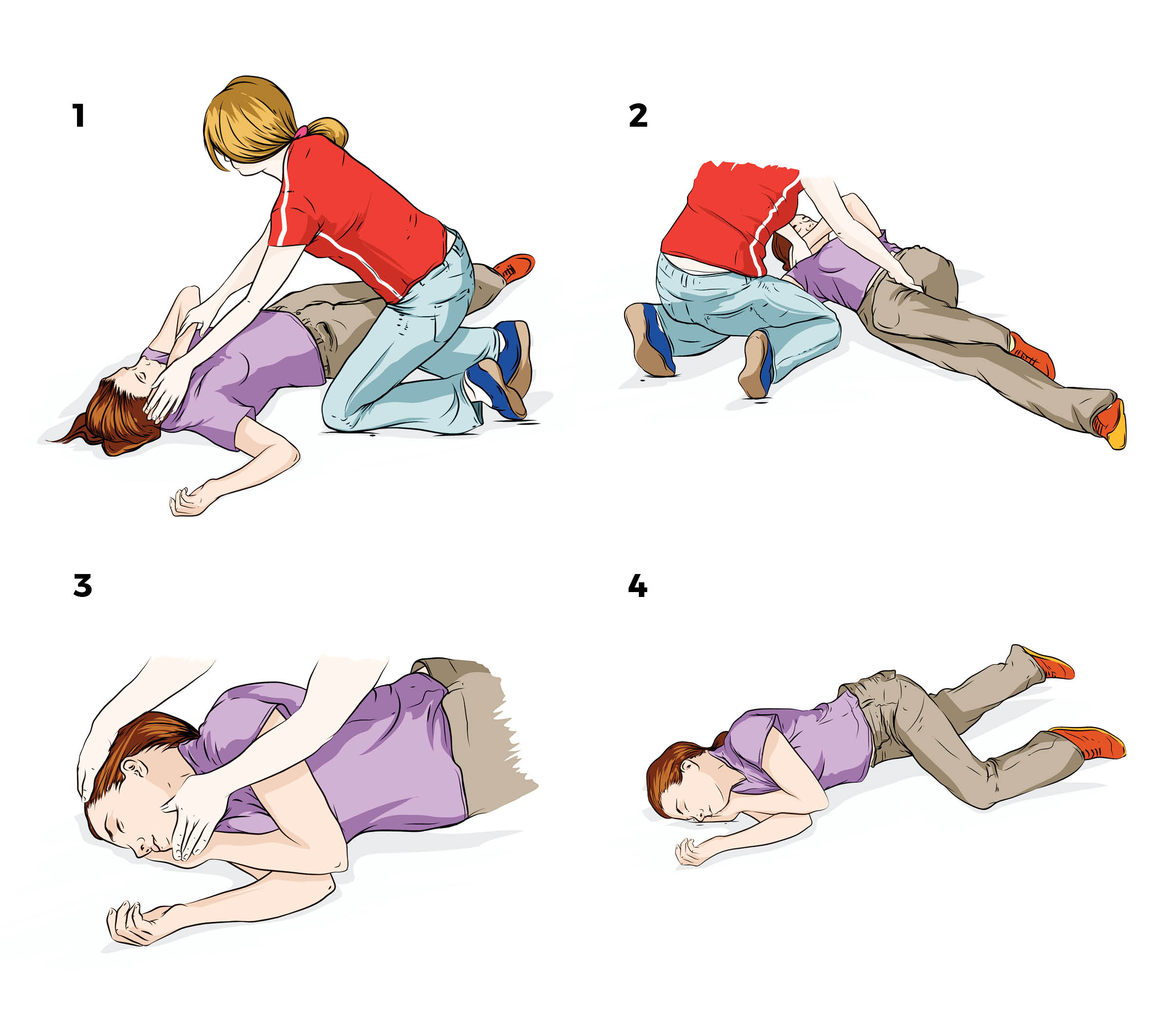
If the person has collapsed or lost consciousness, call an ambulance on triple zero (000). If they have stopped breathing commence CPR. If they are breathing normally, place them into the recovery position.
Adis - Understanding Ketamine Fact Sheet
Adis fact sheet about ketamine, also known as K, Special K, Super K, Vitamin K, Kitkat.
Take a self assessment quiz, it's free and only takes 5 minutes.
